CDC: Precancerous cervical lesions on decline in young women
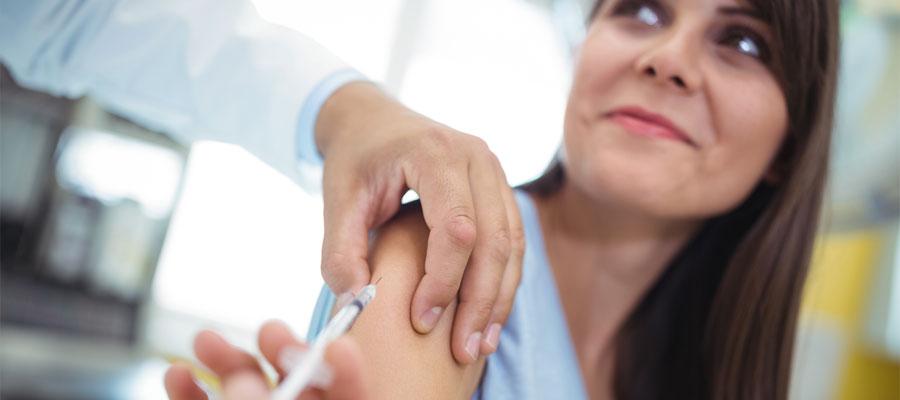
Precancerous cervical lesions associated with human papillomavirus declined sharply in women aged 18–24 between 2008 and 2016, likely reflecting increasing HPV vaccination and changes in detection of these lesions due to updated cervical cancer screening and management recommendations, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported today. Screen-detected, high-grade cervical lesions develop within a few years after infection and have been used to monitor HPV vaccine impact because HPV-associated cancers typically take decades to develop. In 2006, HPV vaccine was licensed and recommended for girls aged 11-12 and for catch-up vaccination through age 26.
Related News Articles
News
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Feb. 9 released its 2027 proposed standards for the health insurance marketplaces, including the issuers and…
Headline
A KFF survey published today found that people view prior authorization as the biggest challenge beyond costs when navigating the health care system. In terms…
Headline
A KFF analysis released Jan. 28 found that Medicare Advantage insurers made nearly 53 million prior authorization determinations in 2024, an increase…
Headline
The AHA Jan. 26 released a white paper on addressing challenges in implementing an advanced explanation of benefits, which requires coordination among multiple…
Perspective
In Elma, Wash., Summit Pacific Medical Center uses innovative approaches to address the region’s significant health challenges, including high rates of chronic…
Headline
The White House released a health care plan Jan. 15 addressing drug prices, health insurance premiums and price transparency efforts. The plan includes…

